The best ways to keep diabetes under control include testing your blood glucose levels regularly, eating small meals, keeping a track of your carbohydrate sources, and exercising regularly. It is also important to check your feet often and maintain your eye health.
Understanding what you should do to keep your blood sugar levels under control, and which lifestyle choices and dietary choices you should make, is essential. [1]
Diabetes is a modern epidemic and affects millions of people around the world, and there is no cure as yet. Once you are diagnosed with this condition, it is essential to manage it properly to reduce the impact on the body.
Being diagnosed with pre-diabetes, type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, or gestational diabetes is life-altering but can be managed with the guidelines discussed in this article.[2]
Ways to Keep Diabetes Level Under Control
Diabetes can have a domino effect on the body and can affect the body negatively in a range of ways, from vision and inflammation of the joints to kidney health and the digestive process. Therefore, implementing a comprehensive lifestyle plan is very important. [3]
Let us look at the most important ways you can manage diabetes.
1. Using Smaller Crockeries with Smaller Meals
Another psychological trick is to prepare your meals on smaller plates. [4]
You are more likely to maintain appropriate portion control and undershoot your levels of calorie and sugar intake, while also having food for later and saving money over the long term.
A popular way is to follow the Diabetes Plate Method, which is simply to fill up half the plate with non-starchy, fibrous vegetables like broccoli or spinach, a quarter with grains or simple vegetables, and the rest with lean protein. [5]
By spreading out 5 or 6 meals throughout the course of the day, your body will remain active in its digestive processes, which increases insulin sensitivity. Furthermore, you will have fewer blood sugar spikes and drops if the caloric and sugar intake is spread out over the course of a day.
You can snack in between your 3 main meals and a bedtime snack is the most important for those who take long-acting insulin at night.
Speaking to a dietitian is also a great way to establish an eating plan and schedule that is customized to your specific needs. [6]
Also, research suggests that a high-energy breakfast helps in reducing hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetics. [7]
It is important to have a healthy breakfast – a combination of at least one carbohydrate choice, fat, and protein.
2. Checking Feet For Ulcers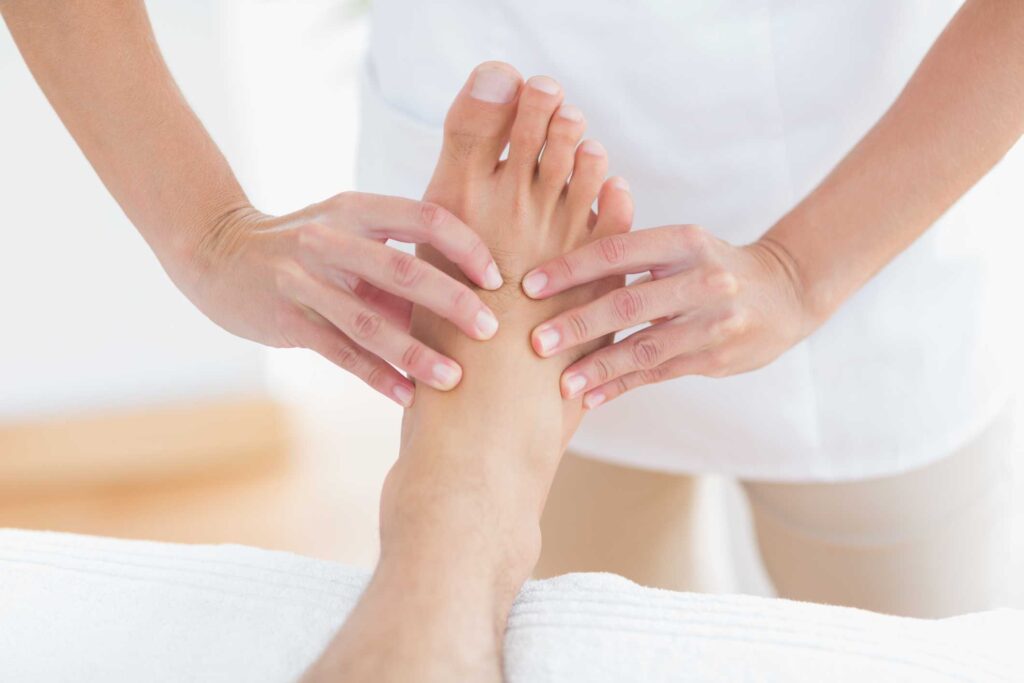
Checking your feet daily is very important due to the risk of developing a diabetic foot ulcer or diabetic neuropathy. Circulation issues in the extremities, particularly the feet, are common for people suffering from diabetes. [8]
This can also result in numbness or lack of sensation, so cuts or scrapes may be completely unnoticed. This sort of minor nerve damage can be dangerous and can lead to infection or more serious foot issues, sometimes even requiring amputation.
Check your feet every day and make notes about any obvious changes in sensation or circulation. Discuss these notes with your doctor at your next check-up.
3. Avoid Drinking and Smoking
Alcohol may contain added sugars that increase blood glucose levels and dehydrate the body. Drink occasionally and in moderation. Have no more than one drink at a time.
Diabetic patients must also quit smoking as nicotine promotes insulin resistance. [9]
Along with creating blood sugar-related problems, it also increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases and kidney problems.
4. Make Healthy Food Choices
Opt for natural sweeteners such as raw honey, stevia, coconut sugar, balsamic vinegar, and dates. They are loaded with minerals and are low in glycaemic load. Such naturally available and easily digestible substances help in managing diabetes effectively. [10]
A high-fiber diet can slow down sugar absorption. Along with giving satiety and aiding in digestion, it also helps lower blood glucose levels. You can get your daily dose of fiber from fruits and vegetables eaten with the skin, beans, legumes, and whole grains like barley, quinoa, and oats.
Fibre also boosts the metabolism, thereby helping to get rid of extra pounds without increasing the calorie load. Fiber ensures progressive absorption of glucose from the intestine and prevents a spike in blood glucose levels.
Probiotics can help to reduce blood sugar levels, insulin levels, and glucose resistance. Probiotics promote healthy gut health which helps in glucose metabolism.
This helps in improving blood sugar levels, prevents inflammation, and improves glycaemic control, normal lipid profile, and blood pressure control in type 2 diabetes.
You may try eating nuts. Nuts contain unsaturated fats, protein, and a range of vitamins and minerals that lower cholesterol, inflammation, and insulin resistance.
According to a study published in the journal BMJ Open, you should include at least 50 grams of almonds, cashews, chestnuts, walnuts, or pistachios in your diet to control blood fats, triglycerides, and sugars. [11]
5. Increase Physical Activities
If you have diabetes, the ADA recommends getting 150 minutes or more of moderate or vigorous physical activity every week. [12]
Instead of trying to pack it all into one or two days, the ADA notes that this should be spread over at least three days with no more than two days in a row of no exercise. As an alternative, if you’re physically able to handle it, you can do at least 75 minutes a week of vigorous exercise, like interval training.
Just like any other element in the weight-loss equation, exercise is not the be-all and end-all here. You typically need a mix of lifestyle changes in order to achieve any weight-loss goals you may have, and even then, some of this is out of your control.
It’s not all about cardio, though. The ADA also recommends doing two to three sessions a week of strengthening, resistance-based exercise on the days you’re not doing aerobic activity. Exercise can sometimes help with weight loss. [13]
Beyond that, exercise can contribute to lowering your blood sugar. Engaging in physical activity makes your body more sensitive to insulin.
This allows your body to make better use of glucose and insulin in the short term, and over time, it can contribute to lower and more stable blood sugar levels.
6. Taking Blood Sugar Test Regularly
Follow your doctor’s advice on how often to check your blood sugar. While symptoms of high or low blood sugar can give you potential clues as to what’s going on in your body, actually checking your glucose levels is the only way to know if you’re within your target range. [14]
Some people with diabetes check their blood glucose levels with a blood glucose meter. This involves poking your finger and putting a drop of blood on a test strip.
Other people use a device called a continuous glucose monitor, which relies on a sensor that’s inserted under your skin. These typically still require you to prick your finger, though.
If you have questions about whether or not you’re monitoring your glucose in the best way for your health and lifestyle, discuss it with your doctor.
7. Reduce Stress
If you’re stressed, you may exercise less, drink more, and not watch your diabetes as closely. Stress can raise your blood sugar and make you less sensitive to insulin.
When you’re stressed, your body adopts a fight or flight response. That means it will make sure you have enough sugar and fat available for energy.[15]
Studies of people with type 1 diabetes found blood sugar levels go up for most people under mental stress and down for others. If you have type 2 diabetes and you’re feeling the pressure, your glucose will go up.
Bottom Line
Controlling your diabetes is a daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly challenge, but the effort is worth it. Right away you’ll feel better and have more energy.
You’ll live better longer with less risk of problems from diabetes like heart attacks, strokes, kidney failure, and even blindness. The key to managing your diabetes is to keep your blood sugar levels as close to normal as possible.